High-sensitivity Troponin-T: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
As of | As of November 12, 2019, the cardiac troponin assay utilized by the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta Regional Hospital (YKDHR) is the Roche Diagnostics [https://diagnostics.roche.com/us/en/products/params/elecsys-troponin-t-high-sensitive-tnt-hs.html ''Elecsys® Troponin T Gen 5 STAT'']. This is a high-sensitivity fifth-generation cardiac troponin assay. | ||
Cardiac troponin assays measure the concentration of either troponin-T or troponin-I. Both high-sensitivity and contemporary troponin assays measure the exact same molecule, but high-sensitivity assays measure ''much'' more precisely and at ''much'' lower concentrations. The high-sensitivity and contemporary assays can be distinguished by the units in which they are reported: Hs-cTnT is reported in ng/'''L''' whereas the contemporary assay (cTnT) is reported in ng/'''mL'''. | |||
:::Conversion between the results can be done by moving the decimal point three places: a contemporary concentration of 0.4 ng/mL is equivalent to a high-sensitivity concentration of 400 mg/mL, and a high-sensitivity concentration of 14 ng/L is equivalent to a contemporary concentration of 0.014 ng/L. This latter conversion illustrates that the high-sensitivity assays accurately measure concentrations which are ''two orders of magnitude'' lower than the assay we were previously using. | |||
Though high-sensitivity troponin assays have been used in Europe and Canada since approximately 2009, the first U.S. FDA approval occurred in 2017. | |||
''NOTE: The information below is not a guideline, but rather excerpts and links intended to augment and/or help develop clinical judgement.'' | ''NOTE: The information below is not a guideline, but rather excerpts and links intended to augment and/or help develop clinical judgement.'' | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 3 December 2019
As of November 12, 2019, the cardiac troponin assay utilized by the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta Regional Hospital (YKDHR) is the Roche Diagnostics Elecsys® Troponin T Gen 5 STAT. This is a high-sensitivity fifth-generation cardiac troponin assay.
Cardiac troponin assays measure the concentration of either troponin-T or troponin-I. Both high-sensitivity and contemporary troponin assays measure the exact same molecule, but high-sensitivity assays measure much more precisely and at much lower concentrations. The high-sensitivity and contemporary assays can be distinguished by the units in which they are reported: Hs-cTnT is reported in ng/L whereas the contemporary assay (cTnT) is reported in ng/mL.
- Conversion between the results can be done by moving the decimal point three places: a contemporary concentration of 0.4 ng/mL is equivalent to a high-sensitivity concentration of 400 mg/mL, and a high-sensitivity concentration of 14 ng/L is equivalent to a contemporary concentration of 0.014 ng/L. This latter conversion illustrates that the high-sensitivity assays accurately measure concentrations which are two orders of magnitude lower than the assay we were previously using.
Though high-sensitivity troponin assays have been used in Europe and Canada since approximately 2009, the first U.S. FDA approval occurred in 2017.
NOTE: The information below is not a guideline, but rather excerpts and links intended to augment and/or help develop clinical judgement.
Cutoffs
Hs-cTnT is considered "positive" when above the gender-specific 99th percentile URL (upper reference range). Per eMail from Scott Cox (YKDHR Director of Diagnostic Services) on 11/10/2019, the following cutoff are recommended for our assay:
| Women | >= 14 ng/L |
| Men | >= 22 ng/L |
A Δ1h (i.e. the change in Hs-cTnT from ED arrival to 1 hour later) >= 3 ng/L is considered positive for acute myocardial injury (AMI).
Per the ACC white paper (see below):
- A single Hs-cTnT >= 100 ng/L is diagnostic of AMI (in the appropriate clinical context).
- When chest pain has been present for >= 2 hours, a single Hs-cTnT < 6 ng/L has been reported to rule out AMI with essentially 100% negative predictive value.
Diagnostic Algorithm
The internet contains several somewhat similar algorithms on reputable medical sites. In particular, the ACEP Webinar (see below, page 16) displays the following diagnostic algorithm:
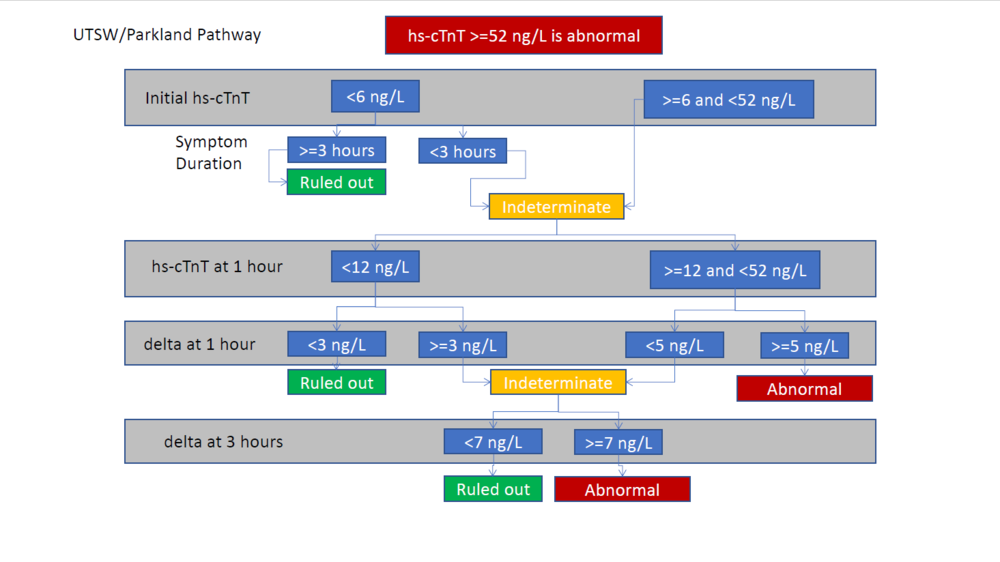
Note that this algorithm does not include risk stratification, such as with the HEART score. Yet the same Webinar contains other algorithms which separate out Hs-cTnT and call the risk stratification a HEAR score (or "modified-HEART" score) and guide diagnosis/management based upon different combinations of Hs-cTnT and HEAR values. Yet other algorithms in the same Webinar recommend skipping risk stratification in those who have low- or high-risk EKG/Hs-cTnT results and only risk stratifying those with intermediate-risk EKG/Hs-cTnT results.
Helpful Links
ACC (American College of Cardiology)
- High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin in the Evaluation of Possible AMI (July 16, 2018)
- SUMMARY: Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (Aug 25, 2018)
ACEP
- Webinar: Incorporating High-Sensitivity Troponin into Your ED
- Critical Issues in the Evaluation and Management of Emergency Department Patients with Suspected Non–ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes (Jun 2018)
MD Calc