Seizures RMT: Difference between revisions
From Guide to YKHC Medical Practices
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''----------------------------------------------------''' | '''----------------------------------------------------''' | ||
[[image:All Emergency RMT.png|750px]] | |||
[[media:pediatric critical care guide.pdf|Pediatric Critical Care Guide]] | |||
----- | |||
==Seizure Evaluation and Treatment== | ==Seizure Evaluation and Treatment== | ||
Revision as of 01:09, 31 August 2019
----------------------------------------------------

Seizure Evaluation and Treatment
- Determine if the patient is still seizing—there may no longer be tonic-clonic movements, but patient may be stiff, have fine tremors, eye deviation (or nystagmus), poor O2 sats, etc.
- Make sure patient is lying down, airway is clear and roll patient on their side if there is vomiting or risk of aspiration
- Start O2 if patient is seizing or sats are low.
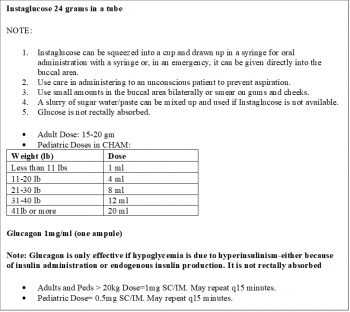
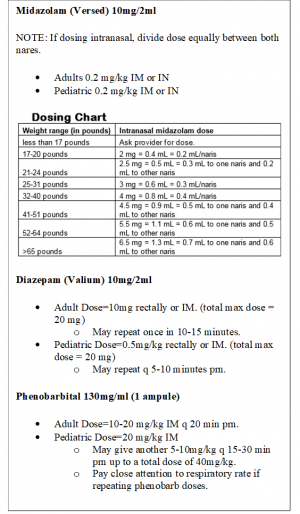
- Have a health aide get Instaglucose, Midazolam, Diazepam, and Phenobarbital out of the village clinic lock box and ready for administering. The health aide can take these with them if they are going off site or have someone go back to the clinic to get them if the patient cannot be moved quickly or safely.
- Have Bag and Mask ready especially for repeat doses of sedating medications
- Get an Accucheck glucose ASAP (low glucose is a reversible cause of seizures) and continue to monitor glucose.
- For low, undetectable, or unknown (no working glucometer) blood glucose--GIVE GLUCOSE ASAP. (see village medications doses in boxes to the right.)
- If seizure does not resolve or is prolonged, activate a medevac ASAP.
- Place IV if possible and give NS bolus as appropriate. Remember, hyponatremia is another reversible cause of status epilepticus; giving a NS bolus may help stop the seizure.
- If a patient has seized for more than 5-10 minutes, be prepared to start with either the patient’s rectal Diastat prescription or the anti-seizure medications in the box below.
- REMEMBER…the longer a patient seizes the harder it is to break the seizure.
- Before giving benzodiazepines or phenobarbital, make sure the health aide has obtained a good fitting bag and mask and is ready to provide assisted ventilation with bag-mask-valve device to support the patient if the patient becomes apneic. Diazepam can be repeated as often as every 5-15 minutes.
- Tiger Text inpatient pharmacist for assistance if needed.
- Take notes with times, medications given, interventions done, and responses.
- Get Vidyo set up for monitoring if not done already if seizure management is ongoing.
- The second line medication will sometimes need be phenobarbital IM. For adults, the dose of IM phenobarb may exhaust the entire village supply!
- If you think there is any chance that the seizure is from infection-Don’t forget to give Ceftriaxone.
- Any emergency RMT requiring a medevac needs to be communicated to the ER physician and PTO completed.