Transcutaneous paCO2 Monitoring: Difference between revisions
From Guide to YKHC Medical Practices
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Transcutaneous CO<sub>2</sub> (TC-CO<sub>2</sub>) monitors function by measuring the CO<sub>2</sub> which diffuses out the skin. Modern TC-CO<sub>2</sub> monitors are a highly accurate, non-invasive method for estimating paCO<sub>2</sub>.<ref name="Nassar2017">Nassar BS, Schmidt GA. [https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201701-034FR '''Estimating Arterial Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide in Ventilated Patients: How Valid Are Surrogate Measures?'''] Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14(6):1005-1014. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201701-034FR. PMID: 28570147.</ref><br> | Transcutaneous CO<sub>2</sub> (TC-CO<sub>2</sub>) monitors function by measuring the CO<sub>2</sub> which diffuses out the skin. Modern TC-CO<sub>2</sub> monitors are a highly accurate, non-invasive method for estimating paCO<sub>2</sub>.<ref name="Nassar2017">Nassar BS, Schmidt GA. [https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201701-034FR '''Estimating Arterial Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide in Ventilated Patients: How Valid Are Surrogate Measures?'''] Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14(6):1005-1014. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201701-034FR. PMID: 28570147.</ref><br> | ||
<br> | |||
[[File:Sentec.PNG|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 21:52, 14 March 2023
Transcutaneous CO2 (TC-CO2) monitors function by measuring the CO2 which diffuses out the skin. Modern TC-CO2 monitors are a highly accurate, non-invasive method for estimating paCO2.[1]
Primary Purpose
YKDRH obtained TC-CO2 monitors for the purpose of monitoring paCO2 trends in patients receiving high-flow nasal cannula or non-invasive ventilation (i.e. CPAP/BiPAP). This was necessary because end-tidal CO2 monitoring is not compatible with these interventions.
Important Points
- Applicable for all age groups (including extremely premature neonates).
- Initial reading requires approximately five minutes to establish.
- TC-CO2 is substantially more accurate than peripheral venous CO2 for estimating paCO2.[1]
- Because CO2 takes several minutes to diffuse out of the skin, the displayed TC-CO2 reading at any given time reflects the paCO2 from 2-4 minutes prior.
- The tracing is a flat line (rather than the waveform created by exhaled air).
- TC-CO2 is used to follow paCO2 trends; it DOES NOT measure instantaneous levels. Therefore, TC-CO2 IS NOT an acceptable substitute for ET-CO2 in situations such as:
- Confirmation of ET-tube placement.
- CPR (neither for CPR adequacy nor ROSC identification).
- Respiratory monitoring during sedation.
- Any situation where monitoring for apnea or any rapid changes in paCO2.
Device
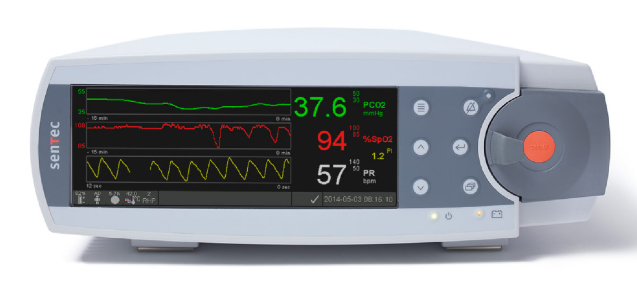
YKDRH has acquired the Sentec Digital Monitoring System.
The Sentec devices provides monitoring of:
- Instantaneous oximetry (with an adjustable duration trend line)
- Instantaneous heart rate (with an adjustable duration trend line)
- Delayed paCO2 (with an adjustable duration trend line)
Resources
Instructional Videos:
- Neonatal Sensor Application for the Sentec Digital Transcutaneous Monitoring System
- Sensor Application Adult Cheek for the Sentec Digital Transcutaneous Monitoring System
PubMed Searches:
REFERENCES
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Nassar BS, Schmidt GA. Estimating Arterial Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide in Ventilated Patients: How Valid Are Surrogate Measures? Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14(6):1005-1014. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201701-034FR. PMID: 28570147.